How to Rank on Google Part 2
How to Rank on Google Part 2
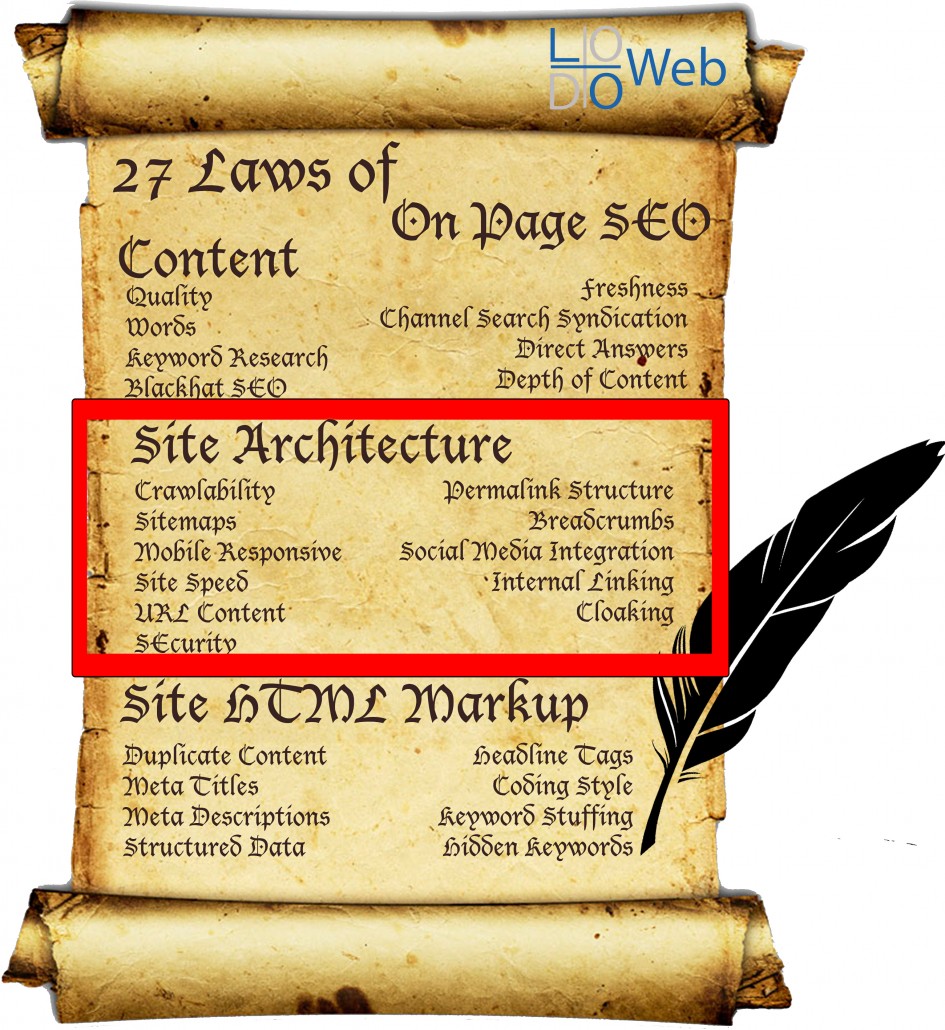
Laws 9-19 of 27 Laws of On Page SEO
It seems more and more these days with the amount of web saturation out there that getting on page 1 rank on Google is the stuff of legend. Though it’s not the easiest thing to do when you have a fresh website, it is possible by following a strategy. The last tutorial went over those things in your control related to content. As we all know by now, Google wants to see fresh, new content. Though the adage content is king may hold true most of the time, it doesn’t necessarily stick when it comes to the technical aspects of SEO. You need more than just good quality content to get recognized by the search engines.
So you’ve created your high-quality, relevant and amazing content, now it’s time to see how we can place it in the best possible website orientation. If the website architecture is not optimized for SEO, it will be more difficult for your site to rank effectively. The goal here is to reduce as much SEO friction as possible so that the search engines have no problem identifying what your content is about.
Part 2
LAWS 9-19 – SITE ARCHITECTURE
LAW 9: CRAWLABILITY
So what is crawlability and why is it so important? Crawlability determines how accessible your site is to the web crawlers. This is essentially notifying the World Wide Web that your site exists and that you are open to receive traffic. Site crawling is the first step in letting the search engines know you exist. If you are restricting crawlers in any way, they will turn around and go elsewhere. It’s imperative that you have an adequate robots.txt file that does not block any crawlers.
Click here to download a robots.txt file that does not block robots.
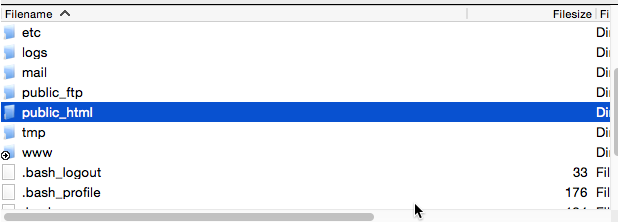 Upload this to the ROOT of your server directory. This should be in the “public_html” folder. You’ll notice that this file is nearly blank. This is intentional. To see a different version, with some blocked content see LoDo Web’s robots.txt file that is uploaded to the root directory. What you block is your call, just remember not to block any root domains to prevent the robots from accessing your site as a whole.
Upload this to the ROOT of your server directory. This should be in the “public_html” folder. You’ll notice that this file is nearly blank. This is intentional. To see a different version, with some blocked content see LoDo Web’s robots.txt file that is uploaded to the root directory. What you block is your call, just remember not to block any root domains to prevent the robots from accessing your site as a whole.
 Another way is to setup up Google Webmaster Tools and do a robots test. This runs a quick test on your root domain, or any other domain you set it to. If your test comes out as “Allowed“, then your robots.txt clears the robots crawlability test.
Another way is to setup up Google Webmaster Tools and do a robots test. This runs a quick test on your root domain, or any other domain you set it to. If your test comes out as “Allowed“, then your robots.txt clears the robots crawlability test.
![]()
If your robots.txt clears Google’s tests, then you should be good. On the flip side, not letting the crawlers access certain pages or folders may be a great idea to limit the amount of information crawled. Remember, we are looking for efficient crawls. Disallowing certain folders and limiting the amount of information crawled will speed up the web crawler’s efficiency and reduce the amount of time it needs to spend there. Perfect.
The amount of time that the crawler may spend on your site is referred to as a Crawl Budget and each site has only a certain amount of crawl budget available. This is very important to consider if you have a large site. You want the right pages crawled. In other words, you want the most important pages on your site crawled first, and the rest to have a lower priority. Core files and plugins are not essential to be crawled and should be disallowed.
In general, your site shouldn’t cause any site crawl issues, especially if you are using WordPress. WordPress comes stock with a built in robots.txt file so you don’t even have to make one. However, if you have certain JavaScripts or Flash applications on your site, this can cause crawling issues.
LAW 10: SITEMAPS
What’s a sitemap? A sitemap is literally that, a map of your site. Consider it a blueprint designed for the crawlers to identify the important areas of your site. Sitemaps are usually in .xml format and are used by the robots that crawl your site. Can they be used by humans? Of course, you can access ours right here. This gives the outline of your site and allows visitors and robots alike to determine the page hierarchy.
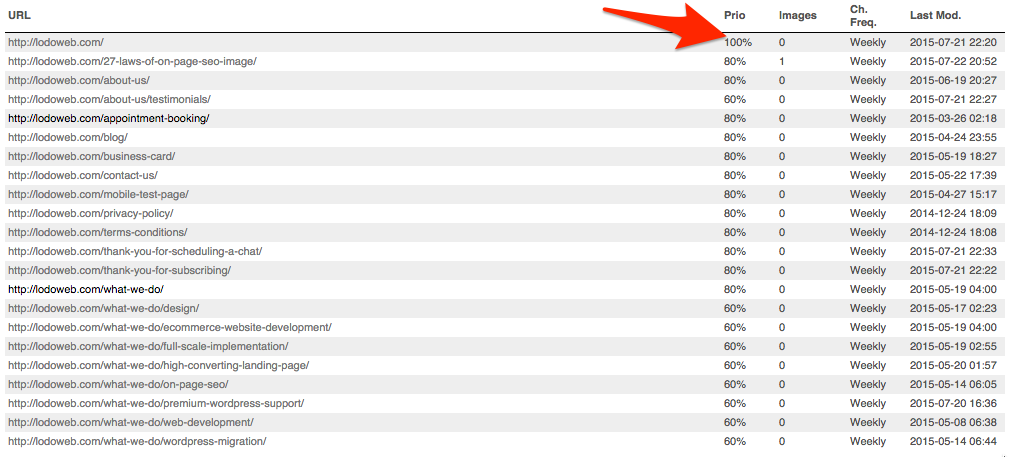 Without a sitemap, crawlers are effectively navigating your site without any guidance or maps. There is no way for them to know where they are on your site and what the index priority is of each page. This indicates hierarchy.
Without a sitemap, crawlers are effectively navigating your site without any guidance or maps. There is no way for them to know where they are on your site and what the index priority is of each page. This indicates hierarchy.
The page hierarchy indicates which page is the most important and which one will get indexed first with the crawler’s available resources. If you are using WordPress, create a sitemap using Yoast’s SEO Plugin. This automatically creates the sitemap.xml file for you, but includes everything. Make sure to configure it accordingly.
Page sitemaps are to be standard with all websites and gives crawlers the blueprint that they need to navigate your site. Without a sitemap, a crawler is like a ship without a rudder, aimlessly navigating until it uses up Crawl Budget and leaves
LAW 11: MOBILE RESPONSIVE
On April 21st Google released it’s mobile algorithm update. It’s official, Google now indexes the display of a site as part of its search algorithm. Being mobile responsive is of utmost importance as you will see your rank plumit compared to your competitors if they are mobile optimized and you are not. So what does it mean to be mobile optimized? Mobile optimization or responsive design means that your site will respond to any device that loads your site. It responds to fit the dimensions of that device in order to optimize browsing for all viewers.
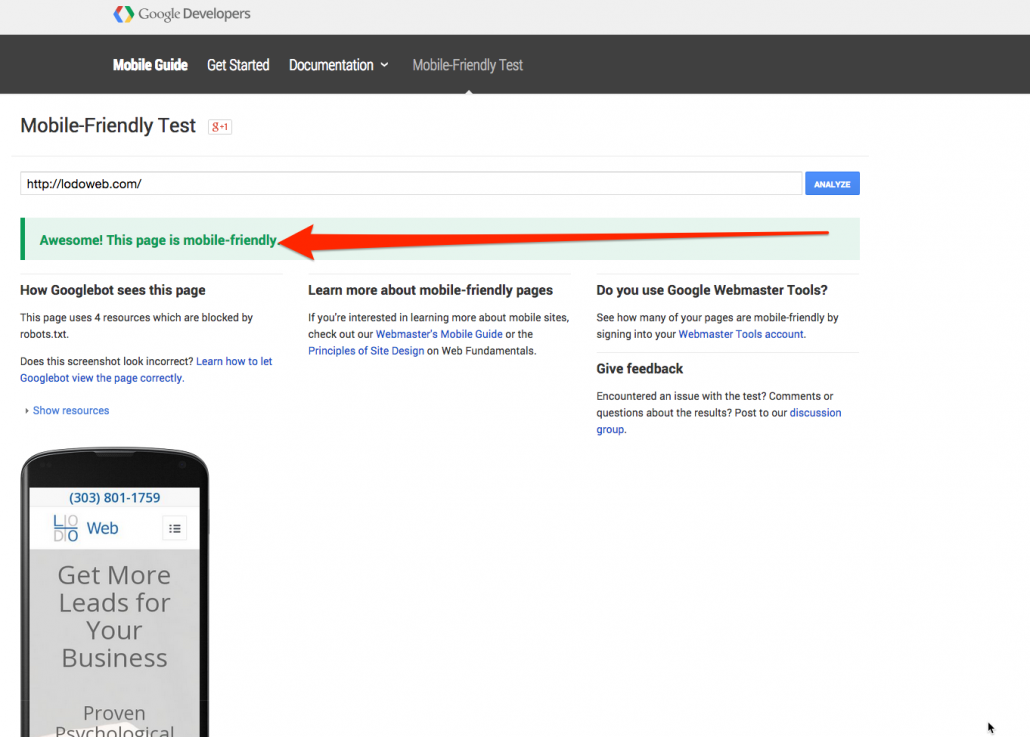 Google has even taken the liberty of releasing a Mobile-Friendly Test tool. If you pass, you should see results like what you see on the left. This handy little test tool allows you to see if your site is mobile responsive and abides by Google’s algorithm updates. If it does, you’ll pass and you’ll also see a little “mobile friendly” signature next to your link when visiting the site on a mobile device.
Google has even taken the liberty of releasing a Mobile-Friendly Test tool. If you pass, you should see results like what you see on the left. This handy little test tool allows you to see if your site is mobile responsive and abides by Google’s algorithm updates. If it does, you’ll pass and you’ll also see a little “mobile friendly” signature next to your link when visiting the site on a mobile device.
What happens if you have a site that is dated and is not mobile friendly? Well, it will fail the test. If your competitors are mobile responsive and you are not, then Google will dish out higher rank to those competitors on the keywords they rank on, and therefore you will lose your position on the SERP. This is even if you have a high authority site. Without being mobile responsive, you risk being dethroned by those under you in rank.
How do you adapt an old site? The easiest answer, is to get onto a CMS like WordPress and build a new one. I know of a great company that can help you with this ;). Mobile responsive design is becoming yet another benchmark that Google is using to identify rank.
LAW 12: SITE SPEED
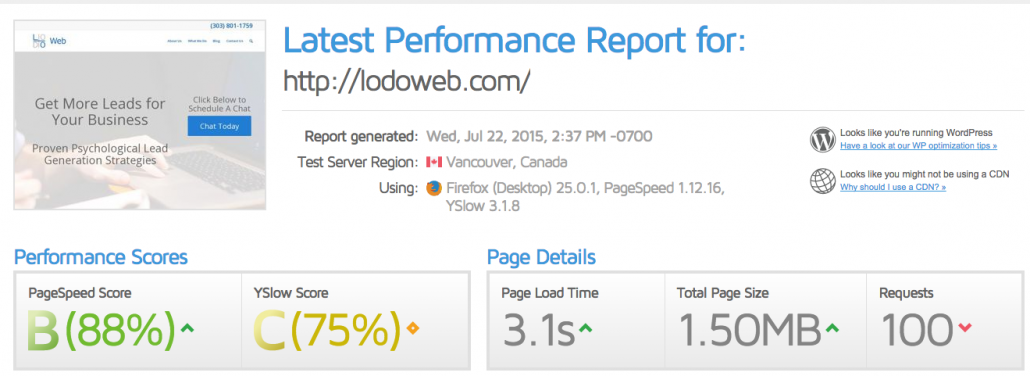 In accordance with responsive design, the page speed load time is also an important consideration for rank. The ages of 56K modems, where you were accustomed to wait about 30 seconds to load a flat HTML page, are gone. Thankfully. It should take seconds to load your site in Google.
In accordance with responsive design, the page speed load time is also an important consideration for rank. The ages of 56K modems, where you were accustomed to wait about 30 seconds to load a flat HTML page, are gone. Thankfully. It should take seconds to load your site in Google.
How fast should your site load? The faster the better, there really isn’t much of a benchmark here. In this case, LoDoWeb.com loads 88% faster than all other websites on the web. That’s pretty solid. The tool that I use to determine site speed is called GTMetrix. This will help you analyze how fast or how slow your site loads compared to the rest of what’s out there. There are certain things, like caching, that can help increase load time, without upgrading your server. Upgrading your server is another way to increase the speed of the site, after all, the site is only as good as the host.
In general, site speed and reduced load time will help improve your rank. The faster the better.
LAW 13: URL CONTENT
Ever heard of Google Sniping? It’s a technique in which you find a keyword you want to rank on and include it everywhere in the site. Let’s say you are trying to rank for “How to Rank on Google”. You would begin by purchasing the domain “HowtoRankOnGoogle.com” and proceed by building out a niche site focused entirely on one keyword. This is a crude example of including information in your links.
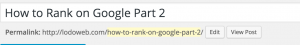 Now, the root domain doesn’t have a whole lot of authority by itself. It does need to be built and optimized. However, the other URLs have a significant impact on rank. That would be every other domain after the root domain. What I’m referring to here is called the permalink. Assuming you did your keyword research correctly, it’s wise to include the keyword in the permalink.
Now, the root domain doesn’t have a whole lot of authority by itself. It does need to be built and optimized. However, the other URLs have a significant impact on rank. That would be every other domain after the root domain. What I’m referring to here is called the permalink. Assuming you did your keyword research correctly, it’s wise to include the keyword in the permalink.
Including the keyword in the permalink and matching that permalink to the page title and to the keyword itself. This will help the search engines identify what your content will be about before even crawling it. This gives a good indication to the crawler, the reader and you. It may seem trivial, but I see this quite a bit where the permalink has nothing to do with the content on the page.
LAW 14: SECURITY
How secure is your site? Hopefully enough to prevent intruders. However, what I’m referring to here is whether or not your site has a Security Socket Layer (SSL) installed. ![]() This gives the “https”, instead of the standard “http” request. An SSL is essentially a certificate of trust between two servers. You usually purchase them and it tells your visitors how “official” you are as a website. With any data that is transferred on your site, it is first encrypted and then sent to the recipient.
This gives the “https”, instead of the standard “http” request. An SSL is essentially a certificate of trust between two servers. You usually purchase them and it tells your visitors how “official” you are as a website. With any data that is transferred on your site, it is first encrypted and then sent to the recipient.
SSL is critical for any transactional based websites, like ecommerce. You must have an SSL if you are selling goods online because you are accepting credit cards. During the transaction, there is a chance that the credit card information can be compromised because of your lack of security.
Having an SSL on your server communicates to your visitors and to the search engines that you are a serious company and take your security and encryption of user information seriously. More link juice to you!
LAW 15: PERMALINK STRUCTURE
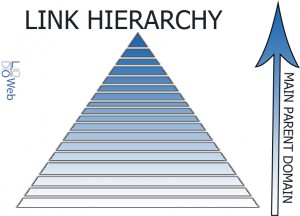 Have you ever visit a site and admire how organized everything is? How every page fits into the other one and it flows quite nicely? This is because of an organized permalink structure. The permalink structure, link structure, or link schema represents the relationship of all your links as compared to the sub pages before them. This goes all the way up to the home page. This has an indication of the overall structure and the actual hierarchical relationship of your links compared to the rest of the links on the site. Now, this is isn’t internal linking, but more so the structured organization of your site. All sites should maintain a hierarchy from the home page and then the parent page and the child page and so on and so on.
Have you ever visit a site and admire how organized everything is? How every page fits into the other one and it flows quite nicely? This is because of an organized permalink structure. The permalink structure, link structure, or link schema represents the relationship of all your links as compared to the sub pages before them. This goes all the way up to the home page. This has an indication of the overall structure and the actual hierarchical relationship of your links compared to the rest of the links on the site. Now, this is isn’t internal linking, but more so the structured organization of your site. All sites should maintain a hierarchy from the home page and then the parent page and the child page and so on and so on.
The correct nesting or hierarchy strategy can help navigate both your visitors and the crawlers. Essentially, you want to have your link structured like a pyramid, with the largest parent page above each child page. A link structure could look something like this: http://www.YOURWEBSITE.com/Parent_Page/Child_Page/Child_Child_Page/Child_Child_Child_Page/etc. As you can see here, there is a clear hierarchy established in relationship to the home page.
Let’s take another look. If you look at LoDo Web’s Full Scale Implementation Page for example, you can see: http://lodoweb.com/what-we-do/full-scale-implementation/. The lodoweb.com portion is the parent page, or home page. The what-we-do portion is the child to the home page and contains all the information about what we do in summary. The full-scale-implementation portion is the child to the what-we-do page and contains more details about what we do, but more specifically the design, development and on page SEO in one bundle. The further you go down into the link hierarchy, or the further you go away from the home page, the more detailed each page gets.
It is important to keep the detailed pages far down the link hierarchy, if they reference the parent page before it. This helps create a logical direction for the link structure of your website. The search engines and humans will know, going back in direction of the link structure should offer them less details than the previous page and perhaps a broader overall view.
This is especially important when dealing with e-commerce. You want to ensure that the product is at the end of all the categories so that the user can go backwards to broader and broader categories, eventually leading back to the home page. Permalink structure goes hand in hand with breadcrumbs.
LAW 16: BREADCRUMBS
 Who’s getting hungry? Who knew we would be talking about food in an article about SEO?
Who’s getting hungry? Who knew we would be talking about food in an article about SEO?
I hate to be the bearer of bad news, but there is no bread in SEO. There are no breadcrumbs to eat. These virtual breadcrumbs represent the location of the user in relation to your site.
Just like Hansel and Gretel left their trail of breadcrumbs in the woods so they can find their way home, the breadcrumbs on your site leave a trail for the visitors so can always find a way back home.
Here’s the important thing, the breadcrumbs should mimic your permalink structure so that the visitor and the crawler know exactly where they are on your site. ![]()
See? you know exactly where you are on the site. You can backtrack and see all the articles associated with each category and eventually find your way back to the homepage. Both the breadcrumbs and permalink structures should be identical in character lengths. They are mirror images, one is the actual link, and the other is used for the navigation of that link. What we are doing with all this site architecture is providing a map and compass to all visitors who are on the site. It gives them direction and relational location on your site.
LAW 17: SOCIAL MEDIA INTEGRATION
With so many social media channels out there, some that you’ve heard of, some that you haven’t it is enough to make you sick. There are literally hundreds of social media channels out there that can be integrated on your site. From feeds to widgets, the integrations are literally endless. I’m sure you’ve heard of the standard: Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Google+, Pinterest. These are by far the most popular channels out there, but there are more that you are probably not aware of. No, I’m  not suggesting to start using all of them. You should certainly have accounts with the main ones, but not all of them. It is a business and personal decision which accounts to have.
not suggesting to start using all of them. You should certainly have accounts with the main ones, but not all of them. It is a business and personal decision which accounts to have.
In any case, your website should be the centralized hub for all these channels. All search engines need to know that your website is the host for all of these social media channels, regardless of how many you have.
All your social media accounts should be linked to your website so that anybody can find access them through the site. This also shows the search engines that all these accounts are linked under one brand name. There is no point in having all these loose accounts dangling around the web, without any linking.
Like a wheel, your website should b at the center of the wheel, with each social media account acting a spoke to the center point on the wheel. Additional to linking each one of these social media accounts externally, linking all your social media accounts with a link to your website in the description, or somewhere on the account, would provide the necessary understanding for search engines to see your website as a higher authority than any of the individual social media accounts.
See social media accounts as an additional outlet of information from your website. Social media is a place where things get shared, and things should originate from your site. Of course, you can always build content on the social media accounts and reference it on your site, but it’s always nice to have everything in once place.
LAW 18: INTERNAL LINKING
Just like external linking, part of Off Page SEO, internal linking offers a way for the search engines to gauge the level of importance in pages. The more links to a particular page on your site, the more it will have perceived importance in ranking. Think about it as internal link juice or link power. Each internal link to another page on your site offers the search engines another way to let them know what you think is the most important pages on your site. Referencing previous articles, or other pages on your site helps the search engines, and your visitors, logically connect your website. It’s like your own internal web within your website.
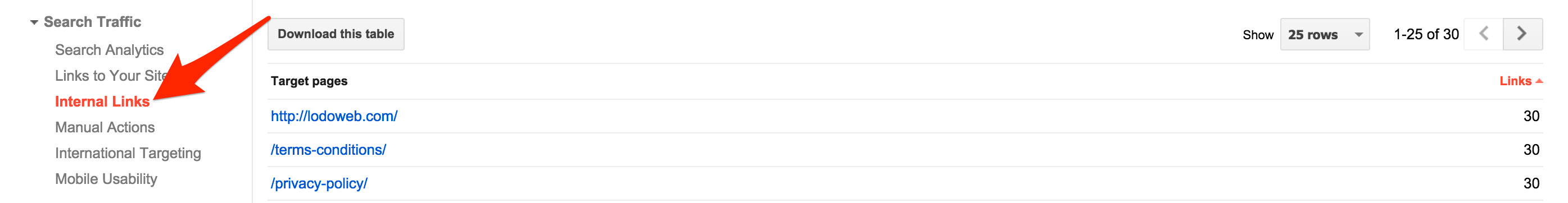 Again, Google has found this important enough to include it in their webmaster tools. This is clear that they find it important enough and you should too. If you ever notice any successful blogs or site, they are always referencing previous posts or pages that already exist on their site. Likewise, each additional link to the site shows the level of importance to the link referenced. Eventually, if you break out your site into the whats linking to what, you’ll see it’ll resemble a web. This web is how search engines can gauge the level of perceived internal authority of individual pages on your site.
Again, Google has found this important enough to include it in their webmaster tools. This is clear that they find it important enough and you should too. If you ever notice any successful blogs or site, they are always referencing previous posts or pages that already exist on their site. Likewise, each additional link to the site shows the level of importance to the link referenced. Eventually, if you break out your site into the whats linking to what, you’ll see it’ll resemble a web. This web is how search engines can gauge the level of perceived internal authority of individual pages on your site.
LAW 19: CLOAKING
There is so much magic in how to rank on Google. From crystal balls, to cloaks. Wait….we aren’t talking about the same thing here. We’re not talking about the cloak that you would put on yourself when you go fetch a pail of water or get milk from the farm. What we’re talking about here is a concept called link cloaking.
Link cloaking is a blackhat method of SEO that shows one link to the search engines and another to the visitors. Often times, the compliant link is shown to the search engines, and a non compliant, sometimes even downright inappropriate link is shown to the actual visitors.
This is accomplished by using a software to identify the IPs of the crawlers and redirect them to a completely different page, whilst your users go to the page you want them to see. This is seen a lot of times in the affiliate world and is a prominent technique in blackhat SEO. Doing this is basically trying to beat the search engine at their own game by giving them a fake page to crawl and therefore rank higher up. When the search engines find out, and they will, your risk your entire IP to get blacklisted on Google and ruin any legitimate reputation you may have had. Recovering from a blacklisted IP on Google is nearly impossible and is often permanent.
But wait, you’re saying you would never attempt something like this because why would you risk your legitimate business on a blackhat technique? Let’s say you have a page 1 rank in Google and you’ve worked your butt off to get there. And let’s just say that you don’t have the right security installed on your site. If a hacker is able to brute force his or her way into your site, you may be in trouble. Once they gain access, they can install a script that would redirect all bot traffic elsewhere and any real visitor traffic to a page of their choosing.
Often times this is a non-compliant page in the eyes of Google. Because they are not the site admin, it doesn’t matter what happens to the IP or reputation of the domain. They are in it for quick cash. By the time you or Google finds out, it’s often to late and they have already done the damage to your reputation. That’s why it’s so important to have good security measures in place on your site.




 We Hate Spam. Your email will never be spammed or sold to any third party company!
We Hate Spam. Your email will never be spammed or sold to any third party company!